2023.12.19
What is Information Security Education? Introduction to Implementation Methods and Material Creation

The modern business environment is increasingly facing evolving threats to information security alongside technological advancements. To protect important data such as customer data, confidential information, and financial information, and to conduct business safely, information security training for employees is essential.
Therefore, this time we will focus on information security education, providing a detailed explanation of its overview, significance, implementation methods, and how to create e-learning materials.
1. What is Information Security Training?

In general, information security training in companies aims to improve the security literacy of each employee in order to prevent security incidents (information security accidents) before they occur.
Examples of security incidents include unauthorized access and malware infections. When these incidents occur, they can pose significant risks to companies, potentially leading to information leaks and data tampering, which can be critical issues for businesses.
To avoid risks, it is important to organize and confirm the approach to business operations and to implement measures that enhance security itself. However, even with a high-level security system in place, it is ultimately humans who use it, so improving security literacy among each employee is essential. Information security education can be said to be one of the most important employee training programs for companies to operate stably and continue to grow.
*The ability to possess knowledge and skills related to information security and to practice them correctly
So, what exactly does information security training entail?
General Information Security Training (Example)
●Threats and Countermeasures When Using the Internet
Explanation of the risks and countermeasures when using internet-based services such as browsing websites, sending emails, and using information devices and mobile terminals.
●Cautions When Disseminating Information
Explanation of precautions and troubleshooting when disseminating information using dedicated platforms available on the internet, such as SNS and blogs.
●Accidents and Damage Cases
Awareness through the introduction of case studies based on actual accidents and damages, and methods for avoiding risks learned from them
Information Security Training for Companies and Organizations (Example)
●Training for All Employees
Explanation of security measures related to each employee, such as password management, virus protection, precautions during telework, and measures when using portable media and devices.
●Training for Organizational Executives
An explanation aimed at executives overseeing the organization regarding the necessity of information security measures, the concept of information security management, and the responsibilities of companies handling personal information.
●Training for Information Management Personnel
In addition to "physical measures" against unauthorized access, viruses, and targeted attacks, explanations of security measures that information management personnel should implement, such as "physical security" related to server management and equipment failure measures, and the introduction and operation of information security policies.
In this way, the content of information security training in companies varies depending on each individual's position and role. It is important for each employee to be aware of their responsibilities and actions to enhance the overall security awareness of the organization and minimize security risks.
2. Risks Associated with Insufficient Information Security Training
In this chapter, we will understand the information security risks surrounding companies and reaffirm the importance of information security education.
●Information security risks include "threats" and "vulnerabilities"
Information security risk refers to the potential for damage or negative impact related to information systems and their data, classified into "threats" and "vulnerabilities."
First, a "threat" refers to a factor that causes risk. There are human-made threats due to human actions and environmental threats such as disasters.
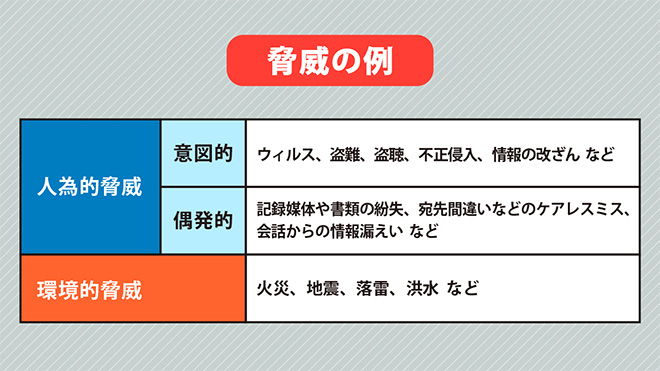
Next, a "vulnerability" refers to a weakness that can be exploited by threats. It indicates "security holes" such as insufficient antivirus protection, software bugs, or unlocked buildings. The greater the vulnerability, the more likely it is to be targeted by malicious attackers, increasing the risk of confidential information being stolen.
●Increasing Damage from Targeted Attacks
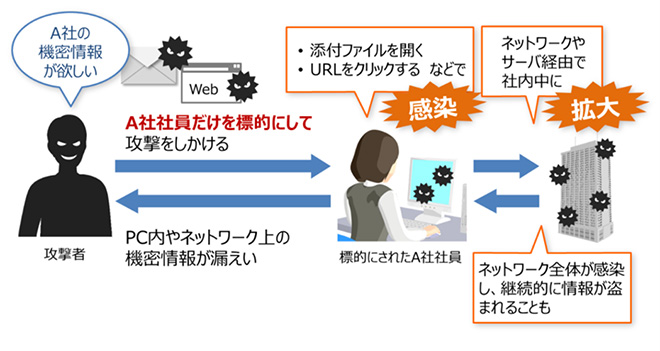
Currently, when it comes to malicious cyber attacks, attacks targeting specific organizations or individuals for financial gain are becoming mainstream. These attacks targeting "specific organizations or individuals" are referred to as "targeted attacks." There are various types of targeted attacks, but one of the most common is phishing emails.
By cleverly luring victims with phishing emails, attackers can infect employees' PCs with viruses, which then spread the virus through the internal network, stealing confidential information or destroying systems. These attacks often continue for long periods, and it is not uncommon to find cases where information has been stolen without the victim's awareness!
●A red flag for business continuity due to loss of trust
Companies hold not only information about their own employees and personal data but also various information about business partners, contractors, and customers. Therefore, if this information is leaked improperly, the company may lose trust, leading to a decline in competitiveness and a fall in its market position. As a result, there may be cases where it becomes difficult to continue business operations.
From the above, it has been understood that insufficient information security training can cause serious damage to companies. Therefore, companies need to conduct adequate information security training to minimize risks.
3. Implementation Methods for Information Security Training
So far, we have explained the overview and significance of information security training, but what steps should be taken when implementing it in a company? We will explain the specific steps.
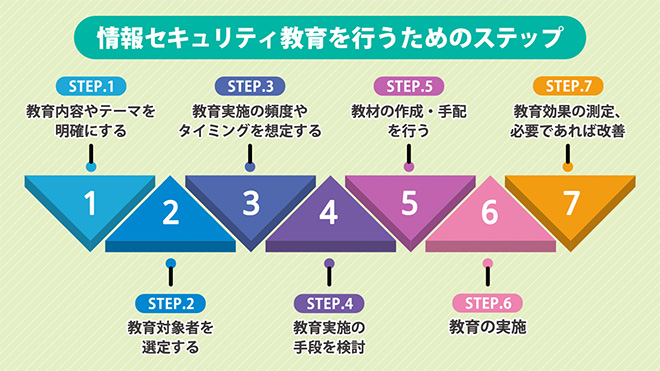
STEP.1 Clarify the Educational Content and Theme
First, let's clarify what you want to be learned through education. In this case, using something broad like general information security is too wide-ranging, so it's best to set a specific theme as much as possible. Even if there is a need to explain knowledge broadly, it is recommended to divide it by theme.
Example) Points to consider when sending and receiving emails > Points to consider when sharing files with external parties > Security risks lurking in telework
STEP.2 Select the Target Audience for Training
Once the content and theme of the training are established, let's select the target audience for the training. For example, determine whether it will be for all employees or limited to specific departments or branches. Defining the scope will make the training content more focused and practical. Additionally, if you designate a person in charge to follow up with each target audience, the operation after the training begins will be smoother.
STEP.3 Consider the frequency and timing of training implementation
Let's anticipate the frequency and timing of training implementation in advance and incorporate it into the schedule so that it can be carried out as part of the business.
(Frequency examples) Every April, once a quarter ... etc.
(Timing examples) At the time of joining, when an incident occurs at a competitor, when internal rules are changed ... etc.
STEP.4 Consider Methods for Implementing Training
Next, let's consider methods for implementing training. The four common methods are as follows.
(1) e-Learning
By utilizing e-learning systems provided by various companies, high-quality education can be easily implemented, and progress management is also easier. However, a network environment is essential.
(2) In-house Training (Group Training)
High degree of freedom, such as being able to implement content unique to the company. Costs for distribution/projected materials, venue arrangements/preparations, and participant transportation will be required.
(3) External Seminars (Group Training)
Deep knowledge can be gained as experts in the field provide explanations. Participation fees and transportation costs will be incurred.
(4) Video materials such as DVDs
Can be used repeatedly and may be duplicated in some cases. However, they are not suitable for fields with a high frequency of updates.
STEP.5 Create and Arrange Teaching Materials
Once you have decided on the means of implementation, let's create or arrange teaching materials accordingly.
If you are preparing existing teaching materials such as e-learning or DVDs, there is no effort in creation, but since the field of information security is constantly changing, it is important to choose materials that reflect the latest information. When creating materials in-house, be mindful to include not only theoretical concepts but also practical examples and scenarios to enhance employees' understanding.
STEP 6: Implementation of Training
Once the preparations are complete, it's finally time to implement the training. Use the prepared materials to instill knowledge of information security in the employees.
STEP.7 Measure the educational effectiveness and make improvements if necessary
When conducting education, tests, interviews with employees (learners), and surveys should be conducted to measure the level of understanding. Based on the results, assess the effectiveness of the education and make improvements to the materials if necessary. Additionally, it is important to provide follow-up support, such as re-education, for employees who score low on tests.
4. How to Create e-Learning Materials for Information Security Training

In the previous chapter, STEP.4, we introduced four methods for implementing information security training, and among them, we particularly recommend e-learning.
E-learning, which can be accessed anytime and anywhere, offers employees an easy way to learn, while allowing administrators to centrally manage learning progress and feedback. Additionally, the interactive elements such as videos and quizzes make it appealing to gain knowledge about information security while having fun.
In addition to utilizing existing materials, there is also the option to create original materials in-house for education using e-learning. Original materials can offer greater uniqueness and provide highly relevant content for employees (learners), which can enhance their appeal.
Here, we will introduce methods for creating e-learning materials for information security training.
How to Create Teaching Materials.1 Create with Power Point
When creating e-learning materials, Power Point is one of the easiest methods. The period from manuscript creation to delivery is relatively short, and by utilizing existing assets (such as materials already prepared for group training), you can create materials more efficiently. Therefore, it is suitable for materials that require frequent updates, such as information security.
〈How to Create Teaching Materials.2〉Create with e-Learning Authoring Tools
e-Learning authoring tools are tools that allow you to easily create interactive teaching materials by combining various media such as text, images, audio, and video. Even without knowledge of programming, it is possible to create high-quality teaching materials easily by utilizing the features. e-Learning authoring tools include "iSpring Suite," an add-in software for PowerPoint, and "Vyond," which specializes in animation.
> iSpring Sales
> Vyond (Animation Production) Sales
How to Create Teaching Materials.3: Outsource to Professionals
This is a method of customizing e-learning materials through vendors (sales companies) that provide them. One of the significant advantages is the ability to create unique materials from scratch with professional support. Of course, it is possible to prepare materials in-house using the PowerPoint and e-learning creation tools mentioned above. However, by utilizing external resources, even for just some parts of the process or materials, you can create higher quality materials more efficiently.
When creating e-learning materials, consider the following points:
① What tools will be used?
② Will it be created in-house or outsourced?
③ File formats (PowerPoint, video formats, animation)
Let's make the best choice that matches the completed image of the teaching materials and various conditions. If you are unsure about your choice, it is also recommended to consult with the vendor and receive advice.
> e-learning material production
5. Summary

In today's digital environment, risks such as cyber attacks and data breaches are always present. To protect companies from these threats, it is essential for each employee to enhance their security literacy, and information security training is a must.
If you have concerns such as "I don't know what kind of education to provide" or "I'm worried if the teaching materials are appropriate," why not consult with a vendor who has specialized knowledge?
Human Science provides comprehensive support for various advice on e-learning, including planning, design, and production of teaching materials. Additionally, we offer the e-learning material "Fundamentals of Information Security Course."
The "Information Security Basics Course" clearly and understandably introduces important points to consider when using computers and smartphones for business, such as software updates and precautions when using free Wi-Fi. The content is general and applicable across various industries, making it widely useful.
For more details, please refer to the e-learning site of Human Science Co., Ltd.
> e-learning material "Fundamentals of Information Security Course"
Contact Information:
Phone Number: 03-5321-3111
hsweb_inquiry@science.co.jp
No Failures!
Key Points for Creating e-Learning Manuscripts
We will focus on the parts of the documents that have already been created, such as materials used in group training, and explain the points to note and areas for revision.

[Content]
- Let's check the workflow.
- Let's brush up the slides.
① Classify and label the information
② Organize and layout the information
③ Brush up