2017.09.27
e-Learning in Corporate Training Basics ① (Introduction)
The "Basics of e-Learning in Corporate Training" series introduces what e-learning in corporate training is all about, starting from the fundamentals. Many of you may already be familiar with this, but I will write it in a way that encourages you to return to the basics and read it.
This time, as part one, I will convey the content that will serve as the premise for the following articles.
Let's get started by first looking at the current state of corporate training in Japan.
The training cost per employee in Japan is 44,892 yen*1 (including e-learning, group training, etc.). In contrast, in the United States, it is 1,252 dollars (approximately 150,000 yen)*2. Although there may be discrepancies due to exchange rates, the cost difference is more than three times.
Employee training (and the resulting improvement in services and quality) is considered essential for the development of a company. Such a disparity in investment could potentially impact the future of Japanese companies.
It is not easy to raise corporate training expenses to the level of the United States, and given the differences in social structure and assumptions, it may not even be necessary. However, the quality of education should be able to improve significantly. To achieve this, I would like to reflect on and review the fundamentals.
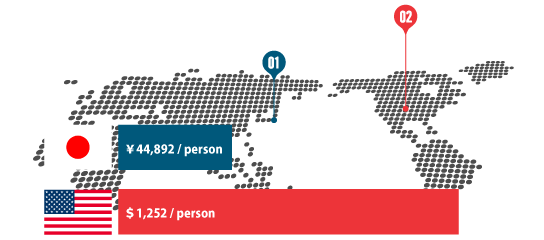
*1 Sanro Research Institute"2016 Fiscal Year (40th) Survey on the Actual Costs of Education and Training"
*2 ATD"Investment in Learning Increases for Fourth Straight Year" (2015 survey, calculated at 120 yen per dollar). This survey includes aspects that differ from the Japanese survey, such as the salaries of employees responsible for talent development.
What is e-Learning?
There are various types of e-learning.
Generally speaking in the industry, it often refers to learning using a Learning Management System (LMS), but broadly, it includes various types of learning utilizing digital devices such as PCs. This encompasses publication on websites, distribution via email with PDFs, distribution on CD/DVDs, and personal learning using resources like Wikipedia and mobile applications.
The content is diverse, but generally, it can be classified into three categories: knowledge-based, skill-based, and attitude-based.
| Compliance, Information Security, etc. | |
| Machine operation techniques, software operation techniques, customer service techniques, etc. | |
| Business etiquette, diversity, environmental education, etc. (Appealing to awareness, mindset, and impressions) |
It is necessary to carefully plan the expression methods and delivery methods according to each classification.
※ Traditionally, "skills" were limited to the acquisition of knowledge for action (+ prompting action), but with the development of the latest technologies such as VR/AR/MR, it is becoming possible to acquire "practical skills" through simulated experiences.
In addition, it can be classified from various vectors.
・Target audience range (for young people, everyone, region-specific, etc.)
・Content type (video, game, quiz, with or without audio, etc.)
・Purpose of implementation (evaluation, skill acquisition, compliance with rules and regulations, etc.)
・Type of learner (in-house employees, BtoB employees, individuals)
Planning the structure, expression, and technologies used in educational materials based on differences in characteristics and purposes is the first step of e-learning materials, known as "planning". If there is a discrepancy in the planning, it can lead to misunderstandings for both the content produced and the learners, resulting in comments like "I don't want to receive this kind of education" or "It's hard to understand."
School Education and Corporate Training
When we talk about "education," it often brings to mind school education, but corporate education is largely adult education and has a significant aspect of human resource development, which greatly differs in purpose and characteristics of the target audience from school education.
| School Education | Corporate Training | |
|---|---|---|
| Characteristics of the Target Audience | Young and Honest | People of all ages and varying levels of motivation |
| Purpose | Achievement of personal goals set by students (e.g., wanting to enter xx school), establishment of basic academic skills, mastery of general knowledge and expertise, vocational training | Achievement of business goals the company wants to achieve, or personal goal achievement (company growth, incentive acquisition, evaluation and technical improvement) |
To improve the quality of adult education,
it is necessary to have not only a system for retention but also a system to motivate and a system to implement. Since it is a one-way e-learning that is not face-to-face or interactive, it is essential to incorporate these ideas effectively. Additionally, employees are not working with the purpose of "learning." It is necessary to motivate not only those who feel a sense of urgency that they must "learn" to do their jobs.
As a foundational theory for this, "Instructional Design" (ID) is utilized.
The second session will focus on instructional design, which is a theory of educational design.

Author:
Keigo Tachino
Education Solutions Department Consulting Unit
・Experience as a training instructor, web designer, etc.
・Engaged in instructional design, e-learning development, etc.
・Learning Designer (eLC certified)
・ATD International Professional Member
Contact Information:
Business Promotion Department Morooka
Phone Number: 03-5321-3111
hsweb_inquiry@science.co.jp
Icons made by Vectors Market from www.flaticon.com is licensed by CC 3.0 BY
Illustrated by http://all-free-download.com/